Page 95 - Demo
P. 95
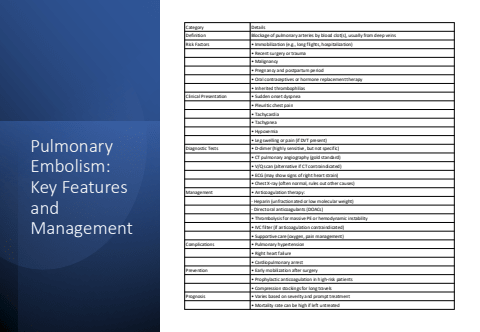
Pulmonary Embolism: Key Features and ManagementCategory DetailsDefinition Blockage of pulmonary arteries by blood clot(s), usually from deep veinsRisk Factors %u2022 Immobilization (e.g., long flights, hospitalization)%u2022 Recent surgery or trauma%u2022 Malignancy%u2022 Pregnancy and postpartum period%u2022 Oral contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy%u2022 Inherited thrombophiliasClinical Presentation %u2022 Sudden onset dyspnea%u2022 Pleuritic chest pain%u2022 Tachycardia%u2022 Tachypnea%u2022 Hypoxemia%u2022 Leg swelling or pain (if DVT present)Diagnostic Tests %u2022 D-dimer (highly sensitive, but not specific)%u2022 CT pulmonary angiography (gold standard)%u2022 V/Q scan (alternative if CT contraindicated)%u2022 ECG (may show signs of right heart strain)%u2022 Chest X-ray (often normal, rules out other causes)Management %u2022 Anticoagulation therapy:- Heparin (unfractionated or low molecular weight)- Direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs)%u2022 Thrombolysis for massive PE or hemodynamic instability%u2022 IVC filter (if anticoagulation contraindicated)%u2022 Supportive care (oxygen, pain management)Complications %u2022 Pulmonary hypertension%u2022 Right heart failure%u2022 Cardiopulmonary arrestPrevention %u2022 Early mobilization after surgery%u2022 Prophylactic anticoagulation in high-risk patients%u2022 Compression stockings for long travelsPrognosis %u2022 Varies based on severity and prompt treatment%u2022 Mortality rate can be high if left untreated