Page 78 - Demo
P. 78
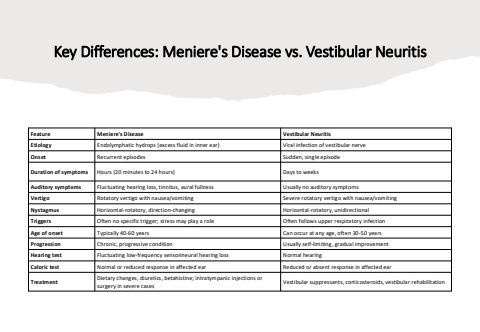
Key Differences: Meniere's Disease vs. Vestibular NeuritisFeature Meniere's Disease Vestibular NeuritisEtiology Endolymphatic hydrops (excess fluid in inner ear) Viral infection of vestibular nerveOnset Recurrent episodes Sudden, single episodeDuration of symptoms Hours (20 minutes to 24 hours) Days to weeksAuditory symptoms Fluctuating hearing loss, tinnitus, aural fullness Usually no auditory symptomsVertigo Rotatory vertigo with nausea/vomiting Severe rotatory vertigo with nausea/vomitingNystagmus Horizontal-rotatory, direction-changing Horizontal-rotatory, unidirectionalTriggers Often no specific trigger; stress may play a role Often follows upper respiratory infectionAge of onset Typically 40-60 years Can occur at any age, often 30-50 yearsProgression Chronic, progressive condition Usually self-limiting, gradual improvementHearing test Fluctuating low-frequency sensorineural hearing loss Normal hearingCaloric test Normal or reduced response in affected ear Reduced or absent response in affected earTreatment Dietary changes, diuretics, betahistine; intratympanic injections or surgery in severe cases Vestibular suppressants, corticosteroids, vestibular rehabilitation