Page 81 - Demo
P. 81
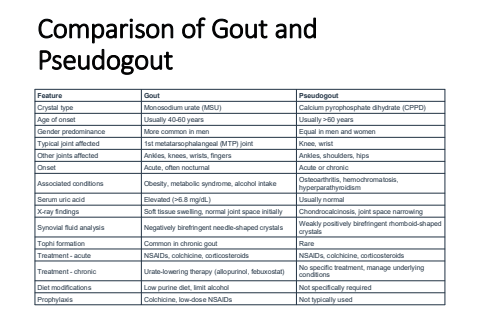
Comparison of Gout and PseudogoutFeature Gout PseudogoutCrystal type Monosodium urate (MSU) Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate (CPPD)Age of onset Usually 40-60 years Usually >60 yearsGender predominance More common in men Equal in men and womenTypical joint affected 1st metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint Knee, wristOther joints affected Ankles, knees, wrists, fingers Ankles, shoulders, hipsOnset Acute, often nocturnal Acute or chronicAssociated conditions Obesity, metabolic syndrome, alcohol intake Osteoarthritis, hemochromatosis, hyperparathyroidismSerum uric acid Elevated (>6.8 mg/dL) Usually normalX-ray findings Soft tissue swelling, normal joint space initially Chondrocalcinosis, joint space narrowingSynovial fluid analysis Negatively birefringent needle-shaped crystals Weakly positively birefringent rhomboid-shaped crystalsTophi formation Common in chronic gout RareTreatment - acute NSAIDs, colchicine, corticosteroids NSAIDs, colchicine, corticosteroidsTreatment - chronic Urate-lowering therapy (allopurinol, febuxostat) No specific treatment, manage underlying conditionsDiet modifications Low purine diet, limit alcohol Not specifically requiredProphylaxis Colchicine, low-dose NSAIDs Not typically used